Contributed By: Supply chain and Logistics Practice, Frost & Sullivan
SAUDI EMERGING AS A LOGISTICS HUB
The largest economy amongst the Gulf Cooperation Council members, Saudi Arabia, is striving to position itself as the logistics hub of the region with its Vision 2030 initiatives. The country aims to establish itself as a logistics hub and further improve its economic stature in line with its Vision 2030. Being at an advantage geographically, Saudi Arabia is located at the centre of the globe falling close to key trade regions such as Asia, Europe and Africa. Leveraging this factor, government initiatives are focused on improving regulatory hurdles, strengthening infrastructural and digital infrastructure which has resulted in its Logistics Performance Rank to reach the 38th position in 2023. The government aims to further improve Saudi’s LPI rank to reach amongst top 10 by 2030 through key strategies and programs:

ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
1 Vision 2030 NIDLP Annual Report 2022 and Economic Cities and Special Zones Authority (ECZA)
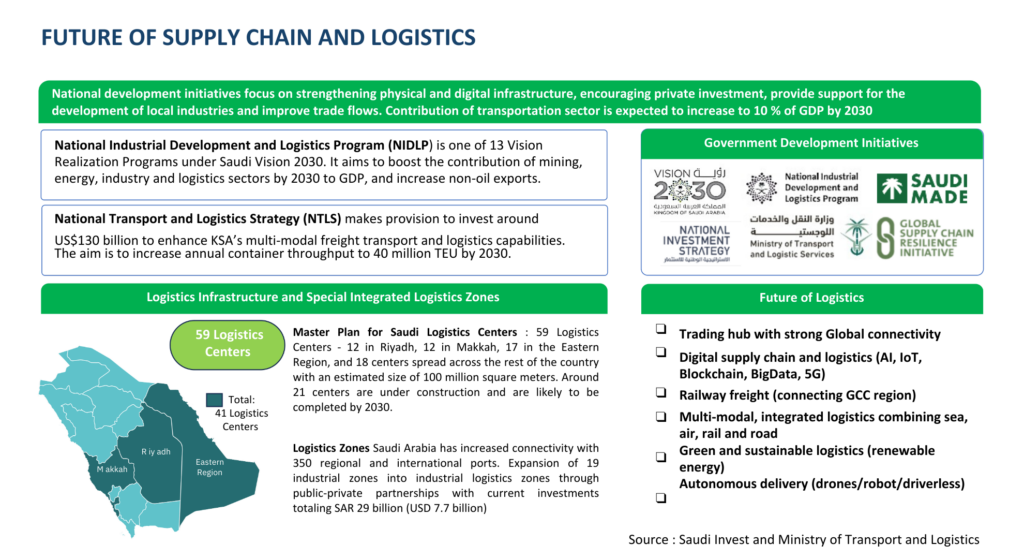
These Government initiatives are expected to support development of transportation infrastructure and improve global connectivity with prospects of expanding the Saudi logistics sector to a market size of USD 57 billion by 2030.
Future growth prospects of the logistics industry are reliant on the extent of success in Saudi’s economic diversification efforts, in addition to its effective implementation of national logistics plans with the participation of both public and private sectors.